Understanding DMAIC and the Six Sigma Belt System
Six Sigma refers to a data-driven process that optimizes business operations through error reduction and quality improvement. At Orage Technologies we provide information about the DMAIC framework and Six Sigma belts hierarchy to help professionals achieve operational excellence and improve efficiency through structured problem-solving and continuous improvement methods across industries.
This guide explains DMAIC methodology together with the Six Sigma belt system. The two methodologies work together to enhance processes while decreasing waste and enhancing quality standards across various industries. The information targets professionals alongside organizations who seek success through data-based approaches.
The fast-paced and competitive business world demands both excellence standards and waste reduction which are no longer optional. Six Sigma emerges as a process improvement system based on factual data. The process improvement framework DMAIC serves as one of the most prominent methods to enhance quality processes.
Six Sigma functions both as a procedural framework and as a community of certified professionals who perform specific duties during project implementation. The Six Sigma system uses a martial arts-based belt hierarchy to assign specific roles to team members. This blog post explains both DMAIC methodology together with the Six Sigma belt system to demonstrate how this proven method transforms business operations.
What Is DMAIC and Why Is It Important?
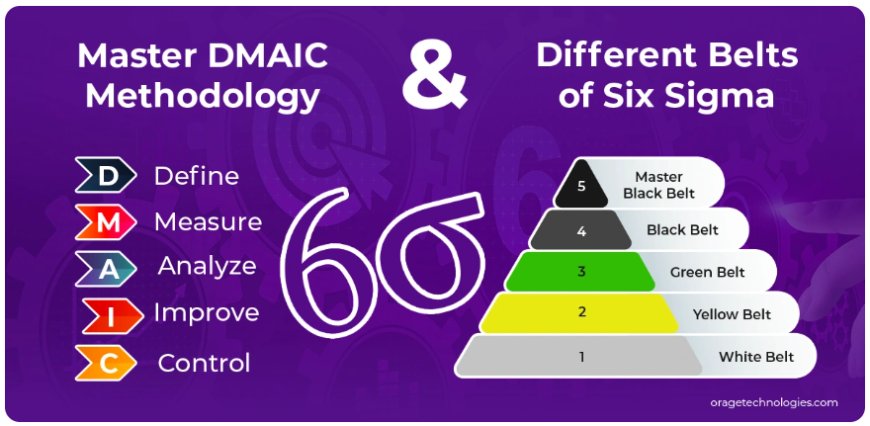
DMAIC is an acronym for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a key tool in Six Sigma for process improvement by defining the problems, proposing solutions, and maintaining improvements over time.
Let's define the five steps:
1. Define Explicitly define the problem, objectives, scope of the project, and the requirements of the customers.
2. Measure Gather data to know current process performance and determine possible metrics.
3. Analyze Analyze the data to identify root causes of defects or inefficiencies.
4. Improve Apply and pilot solutions to the root causes.
5. Control Check the process to maintain improvements and standardize them.
This step-by-step method guarantees that improvements are not only effectively implemented but also measurable and repeatable.
How Does DMAIC Fit Into Six Sigma?
Six Sigma operates as a broad conceptual framework which targets process variation and defect reduction throughout manufacturing and service operations and healthcare services and marketing functions. As one of the main problem-solving methods within Six Sigma, DMAIC functions to achieve process improvement.
Six Sigma receives its framework from DMAIC while using statistical tools and project management practices to achieve its goals. Without DMAIC Six Sigma would lack its structured methodology which delivers its dependable and predictable results.
What Are the Roles Within the Six Sigma Belt System?
Like martial arts, Six Sigma classifies skill and responsibility by belt color. Here's a breakdown:
1. White Belt
* Who it's for: New team members or beginners in Six Sigma.
* Responsibilities: Familiarize themselves with elementary Six Sigma concepts and assist project teams on the local level.
* Training: Limited or initial-level training.
2. Yellow Belt
* Who it's for: Employees involved in smaller project roles.
* Responsibilities: Familiarize themselves with basic DMAIC fundamentals and contribute to data analysis and collection.
* Training: Often includes a couple of days of classroom training or online modules.
3. Green Belt
* Who it's for: Mid-level professionals and team leaders.
* Responsibilities: Participate in small-scale projects through the application of DMAIC under the supervision of Black Belts.
* Training: More thorough, with hands-on use of tools such as process mapping, fishbone diagrams, and control charts.
4. Black Belt
* Who it's for: Project managers and senior professionals.
* Responsibilities: Develop full-scale Six Sigma projects and sponsor Green Belts.
* Training: Mastering DMAIC, statistics, project management, and leadership.
5. Master Black Belt
* Who it's for: Strategic leaders and experts.
* Responsibilities: Mentor and train Black and Green Belts, ensure Six Sigma projects are aligned with business objectives.
* Training: Highly advanced and in many cases requires successful completion of multiple Six Sigma projects.
6. Champion
* Who it's for: Executive sponsors.
* Responsibilities: Fund, resource, and align with organizational priorities.
* Training: Executive summary instead of technical certification.
How Does One Choose the Right Belt?
Your experience, line of work, and the degree of participation you wish to have in process improvement projects determine the suitable Six Sigma belt to choose.
* If you're beginning or seeking foundational knowledge, White or Yellow Belt could be the best.
* To lead little projects or assist in bigger ones, a Green Belt is a suitable second step.
* For complete project leadership or as a consultant, a Black Belt is necessary.
* For becoming a strategic process improvement leader, opt for a Master Black Belt.
Begin with your objectives and present role to choose the most applicable belt certification.
You can also check it out: https://oragetechnologies.com/six-sigma/
What Are the Benefits of Using DMAIC and Six Sigma?
DMAIC together with Six Sigma belt system offers multiple benefits for individuals as well as organizations:
* Process efficiency improves because organizations can optimize their operations by removing wasteful steps.
* Organizations achieve better quality results through lower defect rates which leads to enhanced customer satisfaction.
* Data-based decisions help organizations cut down their expenses by removing unneeded costs.
* Professionals who receive certification from experts become highly valuable to industries across different sectors.
* DMAIC methodology applies to both small and large projects regardless of their location.
The combination of DMAIC methodology with belt system organization creates an effective continuous improvement engine for change management.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is DMAIC Only Used in Manufacturing?
No, DMAIC can be used in any industry such as healthcare, IT, finance, logistics, and even marketing. Any process which can be measured and optimized can be improved with DMAIC.
-
How Long Does it Take to Get a Six Sigma Certification?
* Yellow Belt: A few days
* Green Belt: 2-4 weeks (part-time)
* Black Belt: 1-3 months (part-time or full-time)
* Master Black Belt: 6 months to a year
The duration will vary based on the certifying organization and your availability.
-
Do I Need to Be Mathematically Inclined to Learn Six Sigma?
Whereas Six Sigma does involve statistics, most DMAIC tools that are used (particularly for Yellow and Green Belts) are available to non-technical staff. More advanced belts may expect some familiarity with data analysis, but training courses typically provide all the maths you'll need.
-
Can I Use DMAIC Without Certification?
Yes. DMAIC is a process that can be learned and used by anyone, but having certification adds credibility and formalism to your knowledge.
Conclusion
The DMAIC framework and the Six Sigma belt system provide an organized, repeatable method of addressing real-world business issues. You're an executive who wants to drive profitability, a professional who needs a career boost, or a business leader that wants operation excellence; learning DMAIC and the Six Sigma hierarchy is a solid step in the right direction.
By learning the tools and positions of these, you not only enhance your productivity and analytical capabilities but also play a vital role in your organization's success.